Search engines like to keep an index of last modified pages. They gather data on the page, use external factors and then rank your site accordingly in the search results. If you’re curious about how search engine indexing works and what it is, we’ll be answering these questions in the guide below.
Contents
Is indexing important for SEO?
Yes. If your site or its pages aren’t indexed, they will not appear in the search results. In fact, penalized sites may be deindexed, causing a site to lose 100% traffic from a particular search engine, such as Bing or Google.
What’s the need for indexing by search engines?
Search engines use many resources to crawl pages, store data and rank pages properly. If indexes didn’t exist, search engines would need to crawl billions of pages to find search results.
No one would use search engines if it took 12 hours to answer a query.
However, search engines can produce results to queries in less than a second through internal databases. In a search engine, the index is built by the crawl bot that goes to your site, gathers data and then stores it in a database.
What is indexing in Google?
Google index is a massive database that stores all indexed pages. In fact, the search engine explains indexing succinctly on Google Search Console by saying:
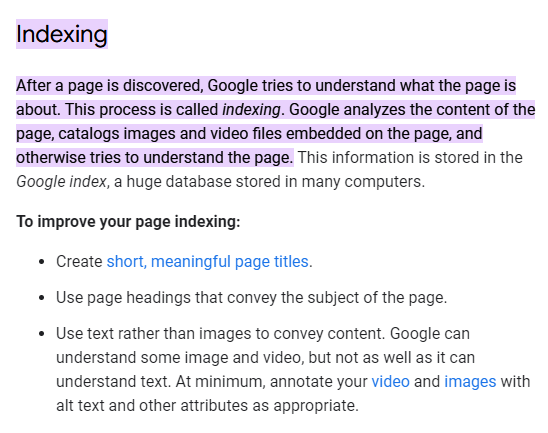
There are really three steps in the indexation process:
Discovery
First, your site or page is discovered by Google. Discovery can happen through a link, social media share, or submitting the page to Google. You can nudge Google to index a page or site by going to Google Search Console.
Sign up for the console, then go to Index > Sitemaps.
Submit your sitemap, and Google will work on crawling the site.
Crawling
Google will add your site to their crawl queue. The platform uses a bot to scan your site, analyze text and try to understand what your page or site is all about. Google will continue following links on your site to try and analyze the entire site if it’s within its crawl budget.
Indexing
Once the crawling process is done, Google will then add its findings to a massive database called the Google Index. However, this is more than an index of last modified sites. The database includes a wealth of information to help Google search if your site’s content matches a question sent through a search query.
Does Google index all pages?
Maybe. Google may not crawl your entire site and index it. Even if it does, it can take weeks to index the pages. You might tell Google to noindex a page, meaning the crawler will not index the site.
Back in 2016, Google stated that they had data for 130 trillion pages that they’ve crawled.
We can assume that the number of pages that Google has information on is far higher today than it was in 2016.
To maximize indexing, you want to make sure you do not have orphan pages on your website. Orphans are isolated pages, that do not have internal outlinks or inlinks.
What is crawling, indexing and ranking in SEO?
In SEO, it’s crucial to understand what crawling, indexing and ranking mean. In short, you can break these components down into the following:
- Crawling is when a search engine bot crawls a website that they discover.
- Indexing is what happens next. Search engines will need to organize and store the data that they gather during the crawling process.
- Ranking is the final step and is where a page ranks for a certain query for one of its indexed pages.
Indexation is crucial to search engine optimization. We know that in a search engine, the index is built by the crawler, and if a page doesn’t get put into the index, it can’t rank for any keywords. Imagine if your main product page doesn’t rank in Google. You would lose revenue.
If your site or page isn’t indexed, this is precisely what would happen.
How PageRank flows through pages
Indexation is also important because PageRank (link equity) will flow through links from one page to another. Imagine if you have 1,000 votes in a contest, but these votes weren’t counted because a judge misspelled your name.
Links are votes for your site and provide equity.
If you have a certain page with 1,000 links and it’s not indexed, you won’t rank for the keywords you’re targeting. Furthermore, link equity won’t flow to other pages.
Let’s assume that you have four internal links on this page, each page would receive 25% of link equity as long as the links are do-follow.
How long does it take for Google to index a page?
It depends. If you don’t submit a sitemap and Google hasn’t discovered your site naturally, it can take a long time for your page to be indexed. In fact, some sites can take six months to be indexed. If you submit a sitemap, this time can be as low as less than an hour to a few days.
Partial indexing
You might see something called “partial indexing” occur, too. Partial indexing involves certain areas of a page not being indexed. Often, duplicate content is the main reason for some sections of a page being indexed and others being ignored.
Index selection
If pages aren’t high quality, Google may decide to keep the content out of their index. In this scenario, you’re facing index selection issues.
Diagnosing your website’s index coverage
If you want to view your site’s index coverage, it’s best to go to the source: Google. Follow these steps:
- Log in to Search Console
- Click the hamburger icon
- Click “Coverage”
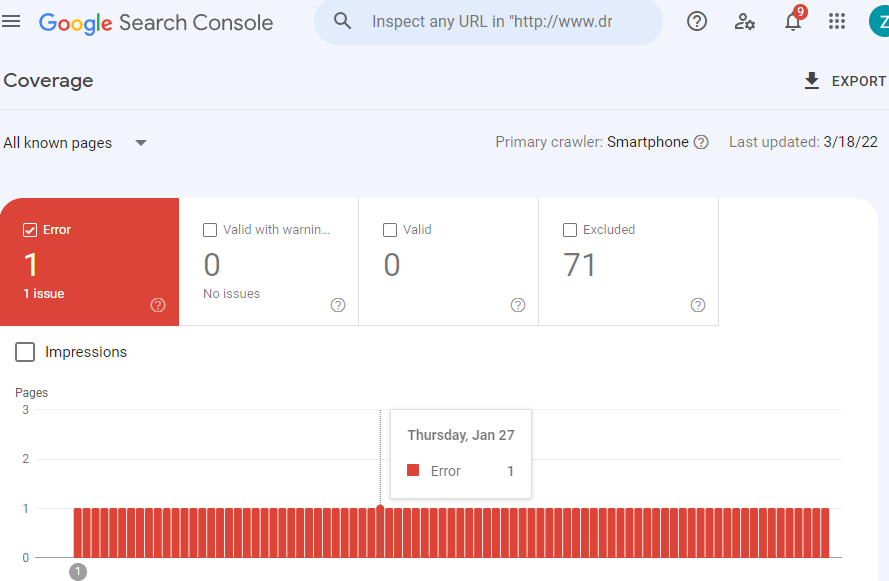
While this site is new with little-to-no content, you’ll see that there are 71 excluded URLs. Most of these pages are generated by plugins or have been marked as noindex while the site is being built.
However, you can see your site’s full index coverage on this page.
What is indexing in digital marketing?
Indexing, as it pertains to digital marketing, is when search engines gather information from your site and then sort it by keywords.
Summary
Search engine indexing is an integral part of your site’s SEO because if your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t rank in the search results. The guide above explains the basics that you need to know to understand indexing and why it’s a crucial part of your site’s search traffic.


