A 400 not found error is frustrating. An end-user cannot reach the resource that they hoped for, and if the site owner doesn’t take extra steps, the person will leave their site. Large and small sites get these errors, and if you get a YouTube 400 error, you can be sure that any website can suffer the same fate. As someone who works in search engine optimization or runs their own website, it’s crucial to master these status codes and take additional measures to control them. We’re going to cover all of the 404 error page codes, what they mean to your site and how to fix them. 
Contents
HTTP Status Codes – 4xx
Most site owners are fine distinguishing a 400 vs. 500 internal server error, but there are a lot of 4xx response codes that don’t include header 403 or 404s. Below is an extensive list of the potential responses you may find in this range.
Understanding HTTP 4XX Client Error Response Codes
You may come across a network error 410 or a 406 error code, but what do these responses even mean? Understanding the meaning of these codes will help you find fixes for them much faster.
- 401 Unauthorized is sent when the request didn’t provide the right authentication credentials.
- 402 Payment Required exists, but it is reserved for future use.
- 403 Forbidden is a common error because the user doesn’t have the authority to view a specific page or folder on a site.
- 404 Not Found or 404 error SEO code is one that means the resource no longer exists. The user either went to an invalid URL or the resource was deleted.
- 405 Method Not Allowed is a call that means the request method sent to the site is not allowed. For example, this response may be sent when an API call tries to access functions that are not allowed.
- 406 Not Acceptable is an uncommon code. A 406 HTTP code means that the server didn’t find content on the site that conforms to the criteria in the request.
- 407 Authentication Required means the proxy must be authenticated for the user to proceed.
- 408 Request Timeout is sent by servers when an unused connection was terminated by the server, often due to inactivity.
- 409 Conflict means that the server and request conflict with each other.
- 410 Gone is a code sent when the resource no longer exists on the server and there’s no forwarding address.
- 411 Length Required is a client issue where the Content-Length header isn’t defined.
- 412 Precondition Failed means preconditions sent to the server are inaccurate
- 413 Payload Too Large means the request is larger than the server allows.
- 414 URI Too Long means the URL is too long to meet server requirements.
- 415 Unsupported Media Type occurs when the server rejects the media type request because it’s unsupported.
- 417 Expectation Failed is an indication that the Expect header failed.
- 429 Too Many Requests means there are too many requests. Oftentimes, you’ll see “there was a problem with the network 429.” What this means is that the user sent too many requests, too fast, and hit the rate limit.
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reason is when the resource cannot be produced, often due to government censorship.
What Does 406 Not Acceptable Mean? The 406 response code is confusing, but it’s often caused by a character set that the server cannot interpret. For the most part, the issue that causes this type of error is on the server side. You can do a few things to fix the HTTP response code 406:
- Check that the URL is formed correctly
- Try multiple platforms to see if the error exists
- Look through logs to see if you can pinpoint the error
- Uninstall or disable new plugins
If the issue exists only after a server upgrade, try rolling back the upgrade to fix it. How to Fix Error 410 Network problem 410 occurs when the resource no longer exists on the origin server. Often, the only way to correct this issue is to restore the resource. Server administrators should verify that the file no longer exists and replace it or put a 301 redirect in place. How to Fix HTTP Code 429 Error 429 too many connections means that the client must wait before sending another request. You can change the server rate limit to a higher amount to fix the issue, but this is often ill-advised. Instead, the user should simply slow down the requests that they send.
What is a 400 Bad Request Error?
One of the most general errors that you can receive is a 400 Bad Request. When you try accessing the resource, something is wrong. Typically, there’s an issue with the request’s header information, or it may be:
- Syntax errors
- Invalid cookies or sessions
- Others
For example, if the 404 redirection doesn’t work for some reason, a 400 response may exist. Server misconfigurations or even trying to upload a file that exceeds server limits may produce this code.
Why You Need a Custom 404 Page / Don’t Ignore 4XX Error Codes
Let’s assume that a user tried coming to your site and received http code 403 from proxy after connect or some other unambiguous response. From a user perspective, the code means that something is wrong, and they’ll often leave the site. If you use a bulk 404 checker, you might be able to find issues and correct them. However, if you have an Ajax 404 issue, tracking down the issue can be even more problematic because you’ll need to do more digging to find the issue. One way to handle 4xx issues is to use custom pages. You can create a custom page for most errors that use a catch-all or specific to certain codes, such as a 404 vs. 410. The main reason you need these special pages is because:
- They alert users to specific issues in a language they understand
- You can instruct the user what to do next
- Search engines can keep crawling your site if the error page links back to it
From a user experience perspective, it’s always best to be sent to a custom page when there’s an error.
How to Create a Custom 404 Page?
First, you’ll want to design the page you’re going to make. You’ll find plenty of free 404 images online on sites, such as:
-
- unsplash.com
- pexels.com
- So much more
 A quick Google search for “404 image free” should also provide you with many great options. Next, it’s as simple as using .htaccess to redirect any errors to a specific page or doing this within your WordPress theme if you are using the platform. Below is an example of using .htaccess to redirect any 4xx statuses you may have: ErrorDocument 404 http://www.example.com/error.html Remember to perform your own 404 test to see what happens when you have an error. A 404 checker bulk can also show you which pages are having issues on your site that need to be fixed.
A quick Google search for “404 image free” should also provide you with many great options. Next, it’s as simple as using .htaccess to redirect any errors to a specific page or doing this within your WordPress theme if you are using the platform. Below is an example of using .htaccess to redirect any 4xx statuses you may have: ErrorDocument 404 http://www.example.com/error.html Remember to perform your own 404 test to see what happens when you have an error. A 404 checker bulk can also show you which pages are having issues on your site that need to be fixed.
- If you need help coming up with ideas for your page, type the following into Google “the best 404 page ever index.”
Do 4XX codes affect SEO?
Yes and no. Inherently, these codes are technical and aren’t used as a ranking signal for your site. You’ll find many people struggling with a YouTube 404 error on Chrome due to a technical issue, and the site never loses its rankings as a result. Search engines expect technical site issues, and every site has them. The famous Twitter error response: status code = 429 is a prime example of some of the world’s top sites having error codes. However, there are a few times when you may lose traffic or some indexation due to these statuses. First, let’s see what the code means in site audits before diving deeper into 404 SEO problems.
What does the ‘4xx page’ error mean in Site Audit?
In a site audit, you may find 404 errors. After all, it’s one of the most common response codes after a migration or through the lifespan of a site. Websites that have user-generated content have tons of these errors because of the high churn rate on the site. Redirecting these pages may not make sense, so teams settle on 404ing it. A WordPress 404 after migration is also something we commonly see because of misconfiguration. Most site audits will list the actual response code so that you can track down the issue and fix it. Refer to the codes and what they mean in the first few sections of this article.
4XX Errors and their negative effect on SEO
There is a lot of emphasis on 404 errors and SEO. If you go into your Google Search Console, you’ll even find that Google lists any issues they find with your site, including 4xx error codes. Obviously, these errors are a big concern and a major reason why people check 404 errors and others. Here are some of the major impacts that can occur:
- Lost rankings. Google and other search engines know that these response codes exist. In fact, you’ve probably seen a YouTube 404 not found error, and Alphabet owns the site. However, most issues won’t impact rankings. If there is a resource or page that’s not found multiple times, it may be removed from the index, which will mean a loss in rankings.
- Poor UX: User experience is an important part of owning a website because it is what keeps users coming back to your site. If the user lands on a 429 HTTP code or another in the 4xx range and there’s no appropriate response to the code, it will impact SEO, leading to high bounce rates and low dwell time.
- Crawlability issues: One thing to consider is that search engine crawlers that come to error pages without any way to navigate back to the site may impact your overall indexation rates.
If your site is bombarded with a bunch of 4xx errors, it doesn’t mean that it will cause your rankings to drop. Here’s Google’s short video on this topic. Google goes on to say that http status codes 410, 404 or any other is fine because it’s a “technical thing.” However, if the page or resource had a lot of SEO value, you may want to redirect it if it’s been deleted to maintain some of the page’s value that you’ve built.
How to Fix a 4XX Error
Once you know how to check a 404 error in website, you may find a slew of other 4xx responses. If you know how to fix crawl errors 404 not found, there’s no easy way to identify the main issue if the resource exists. You’ll need to look deeper in server logs to find the main cause of the error. However, the issue can be resolved most of the time with a quick page refresh. Other options include:
- Checking the URL to make sure it exists
- Fixing any broken links
- Check configuration files
- Verify the server is properly setup
Since there are many configuration issues, it’s impossible to cover them all. Ideally, you’ll look at your Google Analytics 404 report or run a tool to find any errors on your site and then go through each one to correct them. At the very least, if you find a UA 404 or something similar, redirect these pages to an error page that you control. 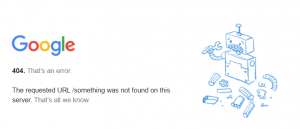 Why? You want to allow the person or crawl bot to go to other pages on your site. Even the Google 404 robot links back to the main site if you click on the image. Otherwise, users won’t know what additional steps to take. Normally, a 404 error fix for free is simply correcting a broken link or URL that’s not typed out properly.
Why? You want to allow the person or crawl bot to go to other pages on your site. Even the Google 404 robot links back to the main site if you click on the image. Otherwise, users won’t know what additional steps to take. Normally, a 404 error fix for free is simply correcting a broken link or URL that’s not typed out properly.
Summary
If you receive an error 404 or a network 410 error, you’ll be able to confidently identify these issues. Of course, if you work in SEO or are a webmaster, this guide has also helped you understand key responses from your site.



