SEO faceted navigation is crucial when running a large enterprise site, primarily in the eCommerce world. For example, you’ll find this type of navigation when you:
- Sort product pages
- Filter out products
However, facets aren’t filters. Instead, a facet is a way to identify unique values for selections. For example, a clothing store may offer you the option to choose gender, product type and style to narrow down results.
One main issue with faceted navigation in SEO is that there’s the risk of generating millions of duplicate pages if you’re not mindful of what’s happening behind the scenes.
If you’re trying to figure out facet SEO and what it means for your site, the following sections will cover the entire concept in great detail.
Contents
What is a Faceted Navigation in SEO?
Shoppers need a smart, logical interface when browsing an eCommerce site. In short, faceted navigation helps eCommerce and directory sites make sense of large result lists. After all, it would be difficult to look through millions of products if there wasn’t a way to logically present them to consumers.
A brief overview of faceted navigation
It’s easier to understand how these navigations work if we take an example from some of the world’s biggest retailers:
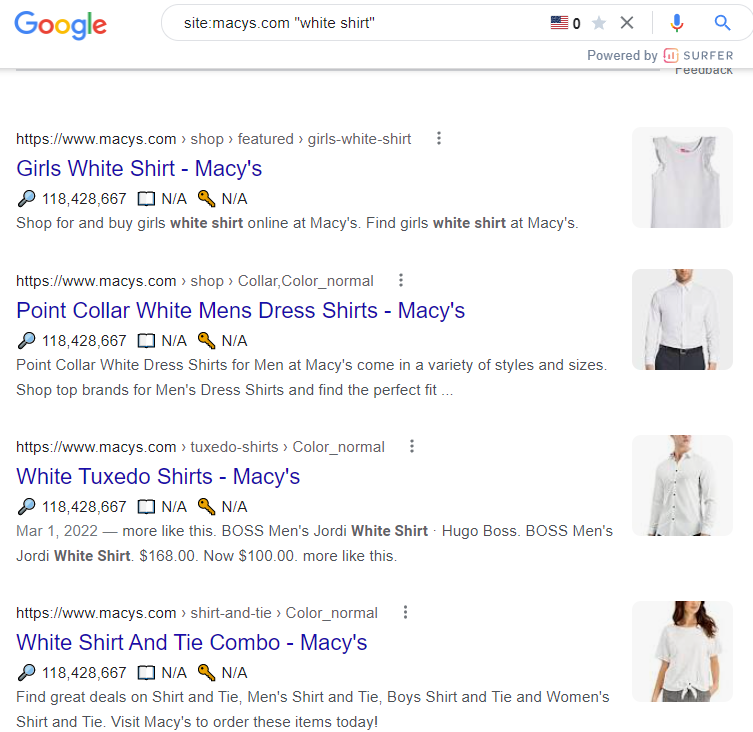
Macy’s
Macy’s has over 1,400 results for white shirts and over 8,000 on the main site. If you’re a consumer navigating through a list of 1,400 shirts, you’re likely going to stop looking when you reach shirt 50 or 100.
The retailer handles this overload by offering facets to navigate the site. Let’s see an example:
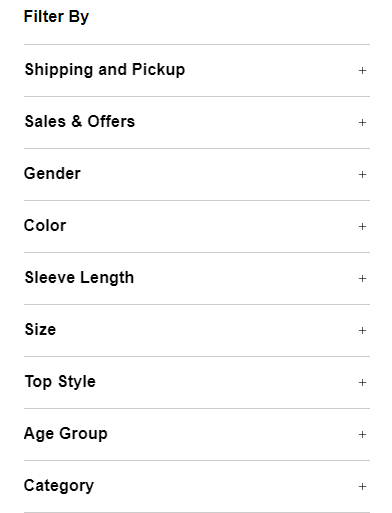
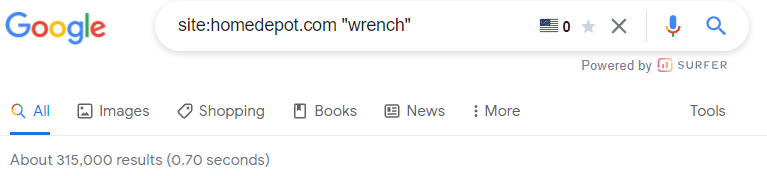
Home Depot
Home Depot also focused on SEO faceted navigation to help users make sense of the large lists of products in their catalog. A basic search for wrenches yields 315,000 results:
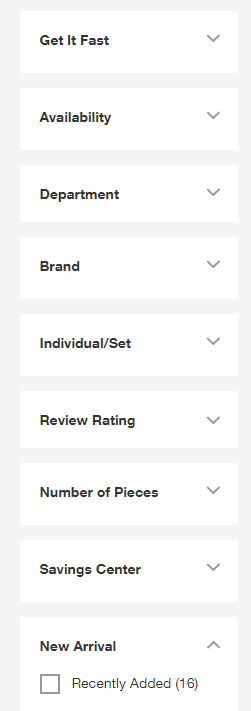
In an effort to make navigation easier for users, the company uses faceted navigation.
What types of websites have faceted navigation?
While eCommerce sites are the first type of site people think of when discussing faceted navigation, you’ll also find this menu style on other site types, such as:
- Classified sites to help narrow listings by location, price, etc.
- Publisher sites to refine content by topic, date, etc.
- Enterprise sites trying to improve user experience.
Any time you have large lists of data, facets may help.
How to audit your faceted navigation for SEO
Audits are crucial to a well-running site. If you’re concerned about your navigation causing issues with your search engine optimization, run an audit on the site. Here are a few ways to begin:
Get familiar with how facets work on your site
Learn the ins and outs of how facets work on your site. You want to know:
- Where facets exist
- How many facets can be added
- If there’s an order to the facets when added to the URL
Evaluate traffic to your faceted pages
Next, take your time to use the information you gathered and evaluate the traffic to these pages. Look through the pages that receive traffic and are being crawled. How many times has each page been visited, crawled, or indexed if it has one, two, three, or more facets?
Identify crawl waste on faceted pages
Look through your analytics and traffic logs to identify any key pages that aren’t receiving the traffic they should be. If you find that one category of your site has three or more facets that are all indexed, they may be wasting your crawl budget, causing other pages not to be indexed.
Identify search demand for your faceted pages
You’ve gathered an immense amount of data, and now it’s time to see if there’s a demand for certain pages. For example, there may be no demand for red wrenches over $200. If your facets allow this level of refinement, they may damage your indexing and rankings.
Check your inventory to understand where you could serve more results to users
You may be able to serve better results to users to help optimize URLs and crawl budget. Be sure to review your inventory to find areas where you can show more results to improve UX and also reduce the risk of crawl budget loss.
What SEO problems can faceted navigation cause?
Google made a post back in 2014 that states that faceted navigation is not SEO-friendly. The main problems that are caused include:
- Crawlers may spend time on duplicate pages, causing them to miss your most valuable content.
- Crawl traps are also a concern, where crawlers fall into the trap of going back to the same core pages of your site.
- Duplicate content is the main issue, but with the right approach, this can be rectified.
- Link equity dilution can occur because hundreds of variations of a single page may exist on a site.
However, due to large data sets, eCommerce must use faceted navigation because it’s the only way to make the UX make logical sense.
Examples of SEO issues created by faceted navigation
“Noindex, follow”
No indexing pages may seem like a smart choice to reduce duplicate content, but noindex doesn’t mean no-follow. Crawl budget will still be lost here due to the bot following links to the page.
Canonicalization
Crawl budget may be wasted if search engines continue to crawl these pages. Additionally, canonical tags may be ignored by search engines. However, most sites still rely on canonical tags as a way to consolidate their link equity.
Disallow via robots.txt
You can use your robots.txt file to disallow certain folders or sections of the site from being accessed. What’s the downside? Link equity becomes trapped.
“Nofollow” internal links to undesirable facets
If you have pages that aren’t important, you may want to nofollow internal links to the page to ensure that you don’t waste crawl budget. However, search engines may still index these pages, causing duplicate content issues.
Other things to consider
Breadcrumbs (and markup) helps a lot
Every subcategory and category page on your site should have breadcrumbs. When you have breadcrumbs, it helps make complex site navigation easier to follow. Also, you’ll nudge Google to crawl the site in a way that you want.
Enforcing a URL order for facet combinations
If facet combinations are not enforced, you may create a long list of the same pages without meaning it. Be sure to enforce the order of the URL, even if that means that some of the facet parameters are empty in the URL.
Summary
SEO faceted navigation is crucial when you have large sets of data or products that must be presented to users logically. If you approach this form of navigation properly, you’ll make the user experience easier for your visitors while also improving sales (if you’re an eCommerce store).



